Demand pricing is the process of determining the price of a commodity based on the desired sales volume. Businesses mostly use market pricing to set the prices of goods sold through different sources at varying rates. This kind of pricing is challenging because it does not always result in the best profit margins as you might anticipate, so as a wholesaler, you should consider the costs of goods and the markups separately so that the prices will not cut deep into your profit margins.
In this article, we will discuss the basics of what you need to know about demand pricing. So, if this is something you are eager to learn about, keep reading!
What Is Demand Pricing?
Demand pricing is a method where prices change based on how many people want a product at a certain time. When a store sees that many people are coming to buy a product, the price may go up. On the other hand, if fewer people are interested, the price may go down.
The basics of demand pricing pertain to: the more the demand is for a product, the higher the price for that particular product will be. On the other hand, the lower the demand for a product, the lower the price for that stock.
This system is built on the idea that the number of buyers can affect the cost. Many businesses use this approach as part of their overall pricing strategies.
Pretty much, the concept is simple. A seller watches consumer demand and then sets prices using a pricing method that reflects that interest. The focus is on how many people want the item and how willing they are to pay. This way, the seller can reach a balance between making a profit and keeping their customers satisfied.
Demand-Based Pricing Definition And Explanation
Demand-based pricing is a strategy that depends on the number of buyers in the market. For example, a company may use dynamic pricing when it adjusts prices as orders come in. This process often involves using a pricing calculator that helps set the right price.
Using demand-based pricing helps B2B sellers to make informed decisions. They do this by watching competitor pricing and comparing their offers with what others charge. In some cases, businesses also use techniques that are related to price discrimination. This means that prices may vary for different groups of buyers. Some may pay more, while others pay less. Hence, using methods such as demand-based pricing and dynamic pricing helps companies choose pricing strategies that suit their market conditions.
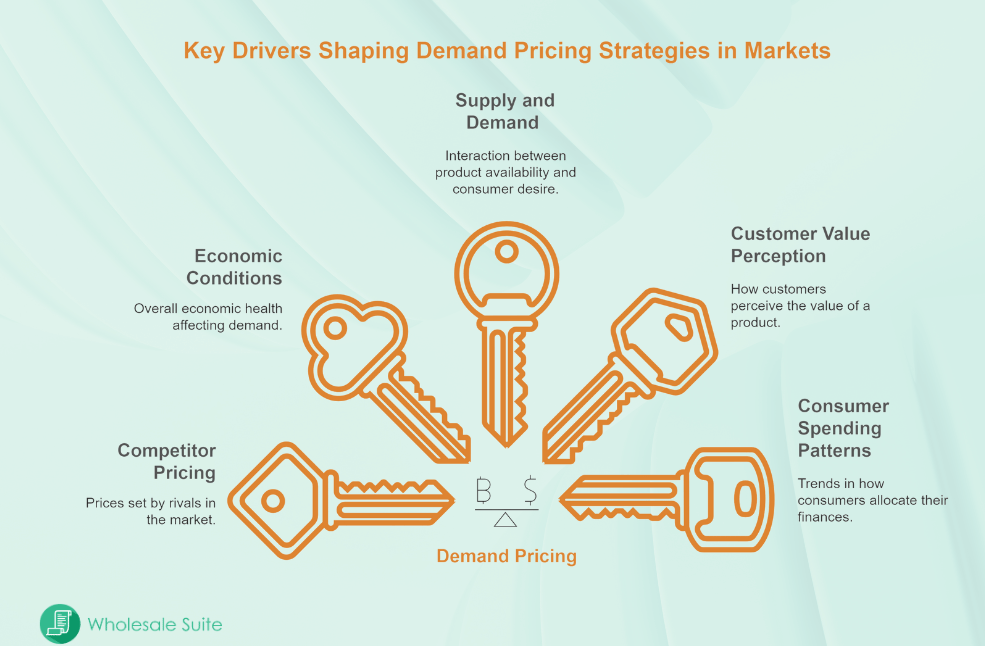
Factors Influencing Demand Pricing
Many factors play a role in how prices are set. In this part of the article, we discuss the elements that affect the pricing method that uses consumer demand.
1. Competitor pricing
Sellers often check the prices that similar businesses charge. For instance, if a shop sees that its competitor has set a low price for a popular item, the shop may adjust its own price. This decision comes from a careful look at competitor pricing.
2. Economic conditions
Economic conditions also affect the pricing method. When the economy is doing well, buyers usually have more money to spend. As a result, prices may be set higher. However, if the economy slows down, people tend to spend less. In this case, sellers may lower their prices to keep up with consumer demand.
For instance, Vogue Business discusses how luxury brands have significantly increased their prices in recent years, leading to consumer fatigue and a slowdown in the luxury market. Additionally, Le Monde highlights the widespread adoption of dynamic pricing across various industries, adjusting costs based on demand and sparking consumer backlash. These reports illustrate how shifts in the economy can influence how companies set their prices.
3. Supply and demand dynamics
Supply and demand dynamics play a big part in how prices change. Sellers look at the number of products available and the number of buyers who want them. When the supply is low and many buyers are ready to purchase, the price goes up. On the other hand, when there is a lot of supply and few buyers, the price goes down. The law of demand holds that demand for a product changes inversely to its price when all else is equal. The higher the price, the lower the level of demand. Businesses use this information to decide on the best pricing strategies.
4. Customer value perception
Customer value perception is about how buyers see the worth of a product. When customers believe an item is very useful or of high quality, they are willing to pay a higher price. Sellers often adjust their pricing method by considering what customers think. This means that when a product is seen as more valuable, the price may rise. In contrast, if a product is not seen as valuable, a lower price may attract more buyers. This approach helps in meeting customer satisfaction.
5. Consumer spending patterns
Consumer spending patterns refer to the habits of buyers when they decide to spend their money. Sellers observe when and how buyers make purchases. For example, during special occasions or holidays, consumer demand may be higher, and the pricing method is adjusted accordingly. If a product is needed for a festive event, many buyers may be ready to pay more. A report shows that spending patterns change during different times of the year. Sellers use these insights to choose the best pricing strategies.
6. Cost structure
The cost structure of a business is also a key factor. This refers to how much it costs to produce and sell a product. When costs are high, sellers may need to set higher prices to cover those expenses. Conversely, if the cost structure is lower, prices can be kept down to attract more buyers. By reviewing their expenses, businesses decide on a pricing method that balances the need to cover costs and keep customer satisfaction high.
Benefits Of Demand Pricing
There are many benefits of using a pricing method that adjusts to consumer demand. In this section, we share five benefits that make this method attractive to many sellers.
Better sales management
Using this pricing method helps sellers respond quickly when many buyers want a product. Prices are adjusted in a way that matches consumer demand. This means that a business can avoid having too many products left unsold.
You may also read: Effective Inventory Management: 5 Strategies To Avoid Overstocks and Understocks.
Improved customer satisfaction
When prices match what customers are willing to pay, they tend to feel more satisfied. Sellers watch consumer demand and use pricing strategies that give buyers a fair deal. In this way, customer satisfaction can be kept high.
Greater flexibility
Sellers using this pricing method can change their prices to suit different market situations. They use pricing strategies that are based on consumer demand and competitor pricing. This flexibility helps the business respond to changes quickly.
Better inventory control
By using a pricing method that adapts to how many buyers there are, sellers can move their products more smoothly. When products do not sell well, the price can be lowered to attract buyers. This approach helps the business manage its inventory.
Clear pricing decisions
A pricing method based on consumer demand makes the decision process more straightforward. Sellers can use data and simple calculations, sometimes with a pricing calculator, to set prices. This clear process means that the business can plan better for future sales.
How Wholesale Prices Premium Supports Demand Pricing For B2B Sales
Wholesale Prices Premium gives businesses the flexibility to use a pricing method that changes with buyer interest within a wholesale model. When prices are set based on consumer demand, customer type, and purchase volume, the business can better handle changes in the market.
Below are some ways Wholesale Prices Premium supports this pricing method:
- Volume-based discounts & demand pricing: Wholesale Prices Premium allows businesses to set tiered pricing based on order quantity. This aligns with demand pricing because businesses can adjust pricing tiers to encourage bulk purchases or optimize profit margins as demand increases.
- Customer-specific pricing adjustments: With Wholesale Prices Premium, businesses can set different price levels for different customers (e.g., VIP buyers, repeat customers, or first-time wholesale buyers).
- Market-driven price changes: Demand pricing means adjusting prices based on market conditions. Using Wholesale Prices Premium, businesses can set pricing rules that automatically adjust wholesale prices based on stock levels, customer groups, or seasonal demand, ensuring profitability even during demand shifts.
- Bundling & volume pricing as a demand strategy: Businesses using Wholesale Prices Premium can implement bulk discounts and bundle pricing, which is a demand-driven strategy. When demand for certain products rises, they can adjust bundle pricing to increase order sizes and move more inventory.
- Encouraging more orders during low-demand periods: Demand pricing is also about lowering prices when demand drops. With Wholesale Prices Premium, businesses can offer time-sensitive discounts, exclusive price breaks for loyal wholesale customers, or flash sales to move slow-selling stock while keeping margins intact.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is demand price?
Demand price is a term used to describe the price set for a product based on how many buyers want it at a given time. In other words, when a product is in high demand, the price goes up. When fewer buyers show interest, the price goes down. This method uses consumer demand as the main guide for setting prices.
How does demand pricing work?
This pricing method works by carefully watching how many buyers are interested in a product. The seller then uses a pricing method that responds to the number of buyers. For instance, when many people want a product, the seller may use dynamic pricing to raise the cost. On the other hand, if fewer people are buying, the seller may lower the price. Many companies use competitor pricing and a pricing calculator to make these decisions.
How to calculate demand pricing?
Calculating this pricing method can be done in several ways. First, the seller may collect data about consumer demand and sales history. Next, they compare this data with competitor pricing and cost structure. After that, they may use a pricing calculator to decide the best price. The seller might also look at consumer spending patterns to adjust the price further. In some cases, the seller uses techniques related to price discrimination to set different prices for different groups of buyers.
Final Thoughts
Setting prices is not just about a fixed number. It is a process where a seller checks the market and watches what buyers do. This method helps sellers plan better when setting prices. It also gives buyers a reason to feel satisfied with their purchase.
Throughout this article, we have given you a clear look at the method where prices change based on the number of factors:
- What is demand pricing?
- Demand-based pricing definition
- Factors influencing demand pricing
- Benefits of demand pricing
- Wholesale Prices Premium and demand pricing
By using demand pricing method based on consumer demand, you can adapt to changes in the market. Decide on the best price for your products and move towards success!
Do you have questions about demand pricing? Let us know in the comments!