You already know that customers come from all kinds of places. Some live near your warehouse. Some live far from any main road. Because of this, you might wonder how to set prices that feel fair for everyone. Many store owners use a geographic pricing strategy for this reason. It helps them set prices that match the real cost of sending orders to each area. This kind of pricing plan is a simple way to keep things steady and clear for your store.
In this article, we will discuss how a geographic pricing strategy works and how it can guide your store. So, you can use this method to set prices for different regions without any stress.
Let’s begin!
What Is A Geographic Pricing Strategy?
Simply put, a geographic pricing strategy is a simple way to change prices based on where the buyer lives. Some places have higher taxes, while some areas require longer delivery trips. Some regions have stronger demand.
Store owners use geographic pricing because each region has its own cost mix. A store may spend more on fuel when sending orders to faraway towns. Another may pay higher storage fees in a crowded city. Some places also follow different tax rules. These small changes affect the final price.
This type of pricing also helps buyers. They get prices that match their local situation.
Why this matters for today’s online stores
A single flat price no longer fits every place and customer location. Because of this, store owners have to check delivery routes, taxes, storage fees, and shipping patterns. They use this to build a pricing plan that fits each group.
Why Online Stores Use Geographic Pricing
Let me walk you through why many store owners use this pricing strategy:
Higher operating costs in some regions
Some areas cost more to serve. That’s just the way it is. A big city may ask for higher rent. A far town may need extra fuel. It is often said, “The map looks small, but the bills say otherwise.” That is why many owners adjust their prices based on local costs.
Different levels of demand and competition
Some places are full of shops, while other areas have very few sellers. When demand changes like this, the price may need to follow the pattern. It keeps the store steady and helps the owner stay smart about each region.
Shipping and fulfillment cost changes
Shipping can feel like a small puzzle. Some routes are simple, while others feel like mini-adventures. These small details affect the cost; that’s why owners should study them before setting regional prices.
You may also read about “WooCommerce Shipping Methods: Which Is Right For Your Wholesale Business?“

Currency changes for global buyers
When a store accepts buyers from other countries, prices can shift quickly due to currency fluctuations. A tiny change in rates can make the store gain or lose money. This is why many stores set different price groups for each country.
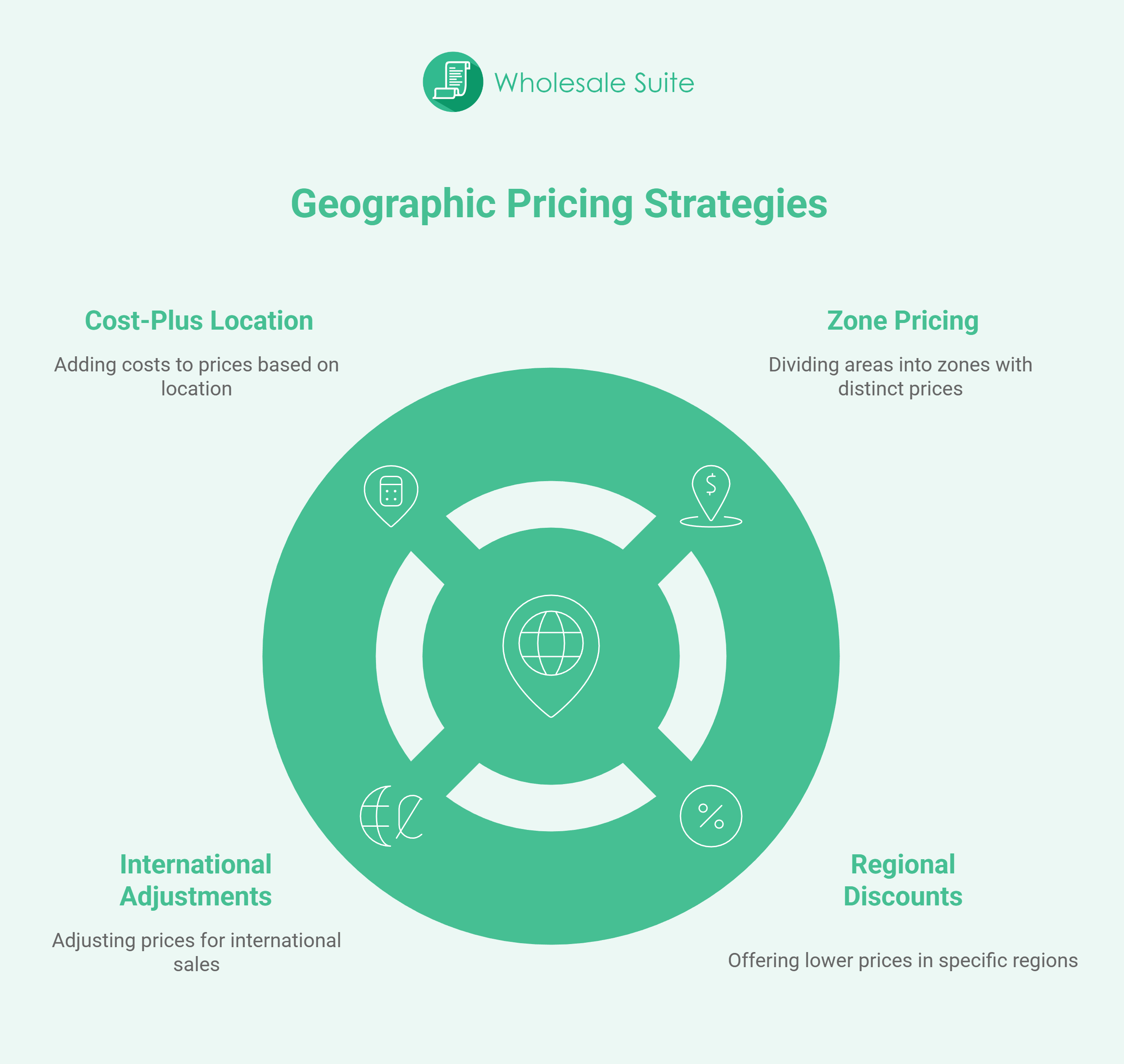
Common Types Of Geographic Pricing Strategies
1. Zone pricing
Let’s start with something you might have already seen without even noticing. Zone pricing groups are placed into simple areas. Think of it like drawing circles on a map. Each circle represents a particular zone. Buyers inside Circle A get one price, while buyers inside Circle B and Circle C get another.
Maybe Zone 1 is near your warehouse. Zone 2 is for buyers in a few towns away. Zone 3 is for far areas that need longer routes. Each zone has its own rate.
Stores use this because it helps them stay transparent about costs. Some zones are closed, so the work needed is small. Some zones are far, so the price rises. It is almost like saying, “If you are near, the trip is chill. If you are far, we need a little extra help.”
2. Regional discounts
Now, let us talk about places where buyers get special prices. These are regional discounts. Some regions have lower income levels. Other regions send many repeat orders. Some even have strong local pickup habits. Stores offer these areas lower prices because it helps both sides. The buyers get a price that fits their daily life, while the store stays steady because the area brings a lot of orders.
Picture a rural area with long delivery routes. If the store wants to support that region, it may offer a lower price to those buyers. Another example is a local pickup spot. If people come to pick up their orders, the store saves on delivery costs, so the price can be lower, too.
3. International pricing adjustments
Now things get a little more interesting. When you sell to buyers from other countries, the numbers move around more. There are different currency rates and taxes that vary depending on the border. There are also duties and local rules. If you sell a product for one price in your country and a buyer from a far country orders it, the final amount changes.
You may also read: 12 Things About International Dropshipping You Need To Know.

If you have ever checked the same product in two countries, you may have noticed that the price differs. One country may have higher duties. Another may have local tax rules. The store adjusts the price to match the actual cost of shipping the item there.
4. Cost-plus location pricing
This one sounds fancy, but it is very simple. The store checks how much it spends in a particular area. Then it adds a small amount on top so it can stay profitable. That is it. Some places have higher service fees, power costs, and tough roads that add wear and tear on vehicles. When owners add these parts together, they make a price that fits that region.
How To Implement Geographic Pricing In Your eCommerce Store
Step 1: Start by mapping your regions
Before you set any price, you need to know where your buyers come from. Think of it like looking at a map and saying, “Okay, this group lives close, while this group lives far. Oh, and this group orders often!”
Most store owners do this with simple tools. They look at their order list, check shipping spots, and review which places order the most. Once they see the pattern, it becomes easier to group each area.
Step 2: Identify your cost differences
Now, here comes the part that owners talk about a lot. Costs change from place to place. When you sit down and list these things by region, you get a more vivid picture. You start to see why a flat price does not work for every buyer. This step alone helps you understand your numbers better.
Step 3: Set clear rules for each region
Once you know your regions and their costs, you can set simple rules.
For example, Zone A might get the base price. Zone B might receive a slightly higher amount due to the longer trip, while Zone C might incur extra fees under local rules. You do not need deep math for this step. You only need a clear guide that you can follow every time.
Step 4: Test your pricing with small groups
Try to test your new prices with a small group first. Check how buyers react. See if the order count stays stable and if the cost fits the work needed in that region. This also gives you a chance to adjust before rolling out the plan to all buyers.
How Wholesale Suite Supports Geographic Pricing For Wholesale Stores
Set location-based wholesale pricing
Many wholesale owners want a simple way to give the right price to each region. This is where a geographic pricing strategy becomes very helpful because wholesale orders do not follow the same pattern as regular orders.
Wholesale Prices Premium helps you set the right price for each area without having to do everything one by one. It lets you create price groups so every region gets a fair amount based on the real cost of serving them.
💚 One thing owners like about Wholesale Prices Premium is how easy it is to create price lists based on your customers’ locations. You can also make a list for high-volume buyers. This fits well with a geographic pricing strategy because you can match each list to the needs of each region. Moreover, Wholesale Prices Premium also lets you set different minimum order rules for each area.
Use Wholesale Payments for smoother checkouts
Payments also change by region. Some places may use certain payment methods more often. Others may not allow some options at all. Wholesale Payments helps you guide each area to the right payment method.
Wholesale buyers often need different payment setups. Some request net terms, while others order large batches and need a smoother process. Wholesale Payments lets you create rules for these needs so each region sees what fits them.
You can also set different rules for fees. Some regions may incur a small handling fee because the payment service costs more there. Wholesale Payments lets you put these rules without doing the math every time.
You may read more about Wholesale Payments here: The Best WooCommerce Payments Plugin For B2B (Full Guide).

Filter buyers by region with Wholesale Lead Capture
Wholesale Lead Capture helps you sort these buyers from the start. You can gather details from new users, check their region, and place them into the right group. This helps you avoid giving the wrong price to the wrong area. It also enables you to keep your regional pricing rules in order.
Utilize Wholesale Order Form for easy bulk buying
Some buyers come from regions that place large orders. Wholesale Order Form gives buyers a faster way to order multiple items at once. This works well with your regional price groups because buyers see the right price for their area while using a clean order page. Many owners say this reduces confusion and helps them maintain steady, large orders.
Best Practices For A Successful Geographic Pricing Strategy
Review your location data every quarter
A geographic pricing strategy works best when your data stays up to date. Shipping routes change. Local rules change. Some regions are starting to order more than before. When you check your data every few months, you can adjust your regional prices to ensure they still reflect the actual work required in each area.
Watch what other stores charge in key regions
Some store owners like to look at what nearby sellers charge. This helps them check if their geographic pricing strategy still makes sense. You do not need to copy anyone. You only need to look at the pattern to understand how other stores handle the same regions.
Adjust prices slowly to avoid surprises
Buyers do not like sudden price jumps. If a region needs a new rate, raise or lower the amount a little at a time. This gives shoppers room to adjust and keep up.
Check buyer feedback by region
Buyers in each region may have their own price comments. Some feel the price fits them well. Some feel confused about fees. When you review this feedback, you can adjust your geographic pricing strategy to better align with what buyers expect.
Check refund and return patterns per region
Every region behaves differently. Some areas rarely send returns. Others send items back more often. When you see these patterns, you can adjust your pricing rules so risky regions do not affect your profit too much.
You may also read: Wholesale Returns: The 5 Great Ways To Handle Refunds.

Keep notes on region-specific issues
Some places have weather problems or slow delivery service. Others may have strict local rules. Keeping notes on these small details helps you update your price groups at the right time.
Conclusion
As you look at your own data, try to treat it like small clues. Each order tells you something. Each region shows a pattern. When you see these signs, you can match your prices to the real cost of reaching each place.
In this article, we discussed how you can do a geographic pricing strategy for your business:
- What is a geographic pricing strategy
- Why online stores use geographic pricing
- Common types of geographic pricing strategies
- How to implement geographic pricing
- How Wholesale Suite supports geographic pricing
- Best practices
When you stay patient with your process, you build a setup that fits your store and supports your long-term plans. If you need more help, you can use the tools inside Wholesale Suite so you can guide your buyers, orders, and pricing in a way that keeps each region easy to manage.
Do you have any more questions? Let us know in the comments!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a geographic pricing strategy?
A geographic pricing strategy is a way to adjust prices based on where the buyer lives, accounting for local costs like taxes, delivery distance, and demand.
Why do online stores use geographic pricing?
Online stores use geographic pricing to reflect actual regional costs such as shipping, taxes, and demand, ensuring prices are fair and sustainable for each area.
How can I implement geographic pricing in my eCommerce store?
You should start by mapping your regions, identifying cost differences, setting clear rules for each region, and testing your prices with small groups before full deployment.
How does Wholesale Suite support geographic pricing for wholesale stores?
Wholesale Suite helps by allowing you to set location-based prices, create regional price lists, manage regional payment methods, and use tools like lead capture and order forms to streamline regional pricing management.
What are the common types of geographic pricing strategies?
The common types include zone pricing, regional discounts, international pricing adjustments, and cost-plus location pricing, each tailored to different regional factors.